Explain How Respiration Differs When Oxygen Is Not Present
List the entry molecules and energy production for all otthe cell respiration pathways. Tap card to see definition.

Image Result For Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Biology Classroom Photosynthesis
Start your trial now.

. Some organisms are able to switch between aerobic and anaerobic modes of respiration based on the environmental. C 6 H 12 O 6 à 2CH 3 CHOH COOH ENERGY 36Kcal. Other organisms perform anaerobic cellular respiration which does not use oxygen.
When oxygen is not present and cellular respiration cannot take place a special anaerobic respiration called fermentation occurs. Less oxygen as it has been used in respiration Gas exchange takes place by diffusion in the alveoli within the lungs. How many ATP are made during anaerobic respiration.
In anaerobic respiration oxygen is not the final electron acceptor at the end of the electron transport chain. Fermentation which does not require oxygen consists of glycolysis followed by a reduction of pyruvate by NADH to produce lactate or ethanol and CO2. Whereas anaerobic respiration takes place in absence of oxygen.
C 6 H 12 O 6 à 2CH 3-CH 2-OH2CO 2 Energy 50 Kcal In the glycolysis of tissues it differs. Assuming enough oxygen is present how many molecules of ATP are produced from a single glucose molecule. Cellular respiration is broken down into two categories.
In anaerobic respiration when free oxygen is not present hydrogen cannot be disposed of by combination with oxygen. Cellular respiration is a process that releases chemical energy from sugars and other carbon based molecules to make ATP when oxygen is present. Explain how you got this total tell me what comes from each stage of cellular respiration - a table may help you explain your answer.
When a respiration goes I absence of oxygen is called anaerobic respiration eg. Fermentation starts with glycolysis to capture some of the energy stored in glucose into ATP. Glycolysis can be either an aerobic or anaerobic process.
The basic chemical reactions for respiration. First week only 499. Calculate the efficiency of the electron transfer to form NADH.
Biology questions and answers. The electron transport chain where the majority of ATP is formed requires a large input of oxygen. Fermentation starts with glycolysis to capture some of the energy stored in glucose into ATP.
Anaerobic respiration differs from aerobic respiration in that. Some bacteria carry out lactic acid fermentation and are used to make products such as yogurt. However many organisms have developed strategies to carry out metabolism without oxygen or can switch from aerobic to anaerobic cell respiration when oxygen is scarce.
Aerobic - C6H12O6Glucose 6 O2Oxygen -- 6 CO2 Carbon Dioxide 6 H2O Water Anaerobic - C6H12O6 Glucose -- 2 C3H6O3 Lactic Acid. The cellular respiration is divided into two different pathways based on presence and absence of oxygen. Explain the difference between aerobic respiration and anaerobic fermentation.
Anaerobic respiration is more energy efficient than aerobic. The production of energy requires oxygen. Aerobic is when oxygen is present and anaerobic is when oxygen is not present.
If cellular respiration occurs in the presence of oxygen it is called as aerobic respiration. It takes place in the mitochondria. Internal respiration here takes place through a different reaction where glucose is only partly broken.
Anaerobic respiration only includes the metabolic pathway of glycolysis. Weve got the study and writing resources you need for your assignments. If oxygen is present the citric acid cycle follows glycolysis with oxidative phosphorylation.
A What is the role of oxygen in the aerobic respiratory pathways and b What would happen if oxygen is not present in the process. Oxygen is present in aerobic respiration as the final electron acceptor where an electron and a proton are transferred to oxygen reducing it to water. Glucose C 6 H 12 O 6 6 O 2 6 CO 2 6 H 2 O 38ATP Aerobic respiration.
It occurs outside of the mitochondria Cellular respiration uses oxygen occurs in the mitochondria and results in a higher yield of ATP. The aerobic respiration is produced more energy and more ATP 38 ATP. When oxygen is not present and cellular respiration cannot take place a special anaerobic respiration called fermentation occurs.
Aerobic organisms or organisms that consume oxygen perform aerobic cellular respiration which does require oxygen. Aerobic respiration takes place in presence of oxygen. If there is no oxygen present then the cell does either alcohol or lactic acid fermentation.
Oxygen is required for cellular respiration it is an aerobic process. As a result the composition of inhaled and exhaled air is different. Anaerobic respiration occurs in the absence of oxygen or when there is not enough oxygen being transported to the cells like during exercise.
Glycolysis which means sugar splitting is the initial process in the cellular respiration pathway. When no oxygen is present the anaerobic processa process that doesnt require oxygen called fermentation begins creating ATP in smaller amounts. I Fermaentation in the yeast ii Respiration by microbes iii Glycolysis in tissues.
Aerobic Respiration and Anaerobic Respiration. Solution for Describe how respiration differs when oxygen is present when oxygen is not present. When oxygen is present glycolysis continues along the aerobic respiration pathway.
Carbon dioxide and water are the end products of aerobic respiration while alcohol is the end product of anaerobic respiration. Oxygen for example is a major factor respiration proceeds by different mechanisms in aerobic conditions or conditions in which oxygen is present than in anaerobic conditions or conditions in which oxygen is not present. The electron transfer chain therefore stops working and no further ATP is formed.
If oxygen is not present then ATP production is restricted to anaerobic respiration. If oxygen is not present anaerobic respiration takes place producing ATP molecules.

Cellular Respiration Chapter Ppt Video Online Download

Respiration Types Atp Human Respiratory System Videos Examples
Where Does The Oxygen Used In Cellular Respiration End Up Quora
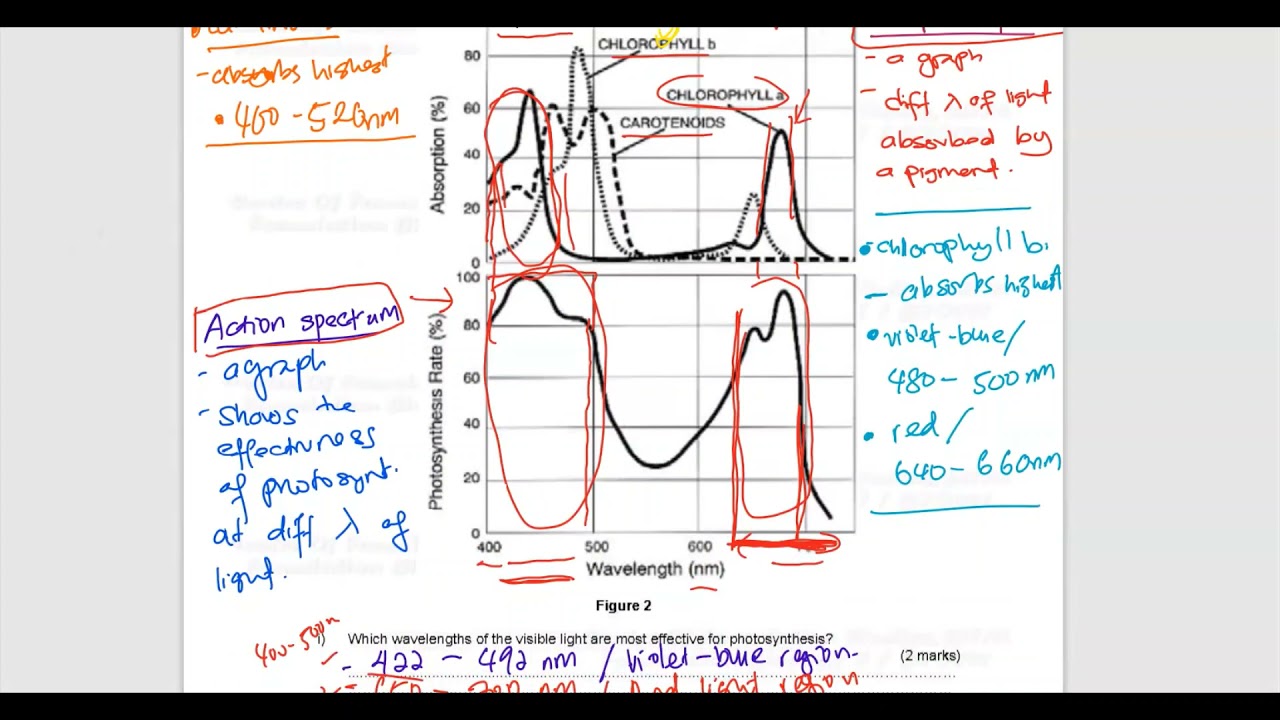
What Will Occur If Oxygen Is Not Available In Great Enough Quantity During Cellular Respiration Lisbdnet Com

What Is The Difference Between Aerobic And Anaerobic Glycolysis Pediaa Com Atp Biology Biochemistry Eukaryotic Cell

Cellular Respiration Review Article Khan Academy

Cellular Respiration An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Aerobic Vs Anaerobic Respiration Advanced Ck 12 Foundation

Cellular Respiration Definition Equation Cycle Process Reactants Products Britannica

Cellular Respiration An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Unit 2 Chapter4 Section 4 5 6 Flashcards Quizlet

Origins Of Cell Compartmentalization Ap Biology Biology Dictionary

Anaerobic Respiration The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary

Pin By Sanghita Dey On Cbse Class 10 Oxygen Oxidation Bullet Journal
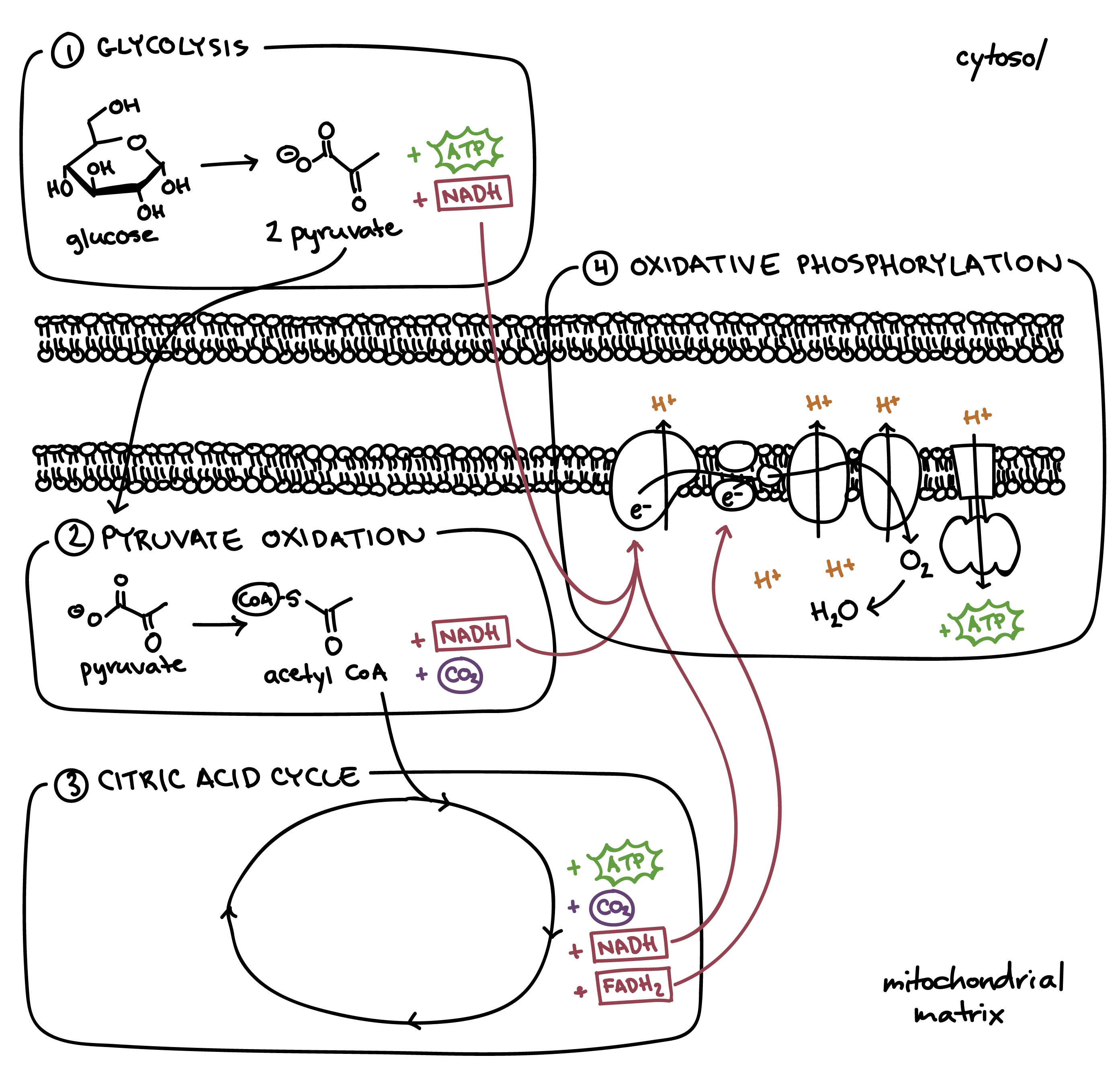
Steps Of Cellular Respiration Biology Article Khan Academy

Cellular Respiration Takes In Food And Uses It To Create Atp A Chemical Which The Cell Uses For Energy

Gas Exchange Anatomy And Physiology Ii

Aerobic And Anaerobic Respiration Nice Big Picture Diagram Anna Totten Totten B Remind Anaerobic Respiration Medical Laboratory Science Student Biochemistry

Comments
Post a Comment